
A. Iwase et al., 2024/Tokyo Metropolitan College
When Japanese scientists needed to study extra about how floor stone instruments relationship again to the Early Higher Paleolithic might need been used, they determined to construct their very own replicas of adzes, axes, and chisels and used these instruments to carry out duties which may have been typical for that period. The ensuing fractures and put on enabled them to develop new standards for figuring out the seemingly features of historical instruments, based on a recent paper revealed within the Journal of Archaeological Science. If these sorts of traces have been certainly discovered on real Stone Age instruments, it could be proof that people had been working with wooden and honing strategies considerably sooner than beforehand believed.
The event of instruments and strategies for woodworking functions began out easy, with the manufacture of cruder instruments just like the spears and throwing sticks widespread within the early Stone Age. Later artifacts relationship again to Mesolithic and Neolithic time durations have been extra subtle, as individuals realized how one can use polished stone instruments to make canoes, bows, wells, and to construct homes. Researchers usually date the emergence of these stone instruments to about 10,000 years in the past. Nevertheless, archaeologists have discovered numerous stone artifacts with floor edges relationship way back to 60,000 to 30,000 years in the past. Nevertheless it’s unclear how these instruments might need been used.
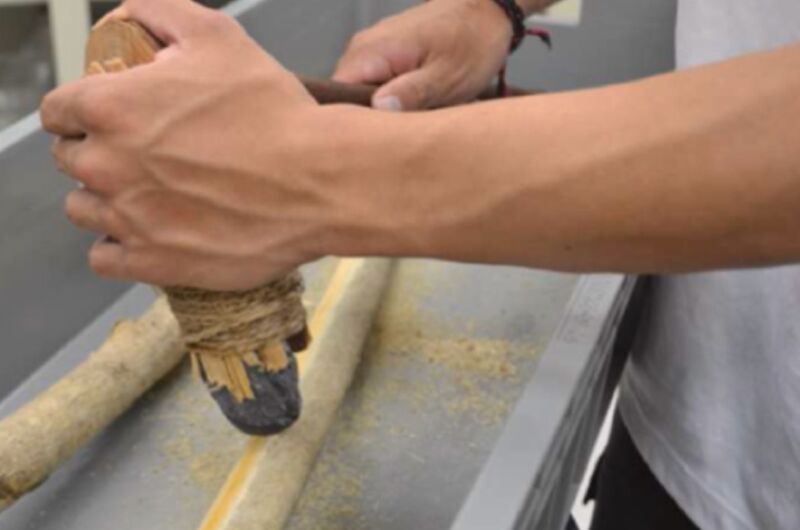
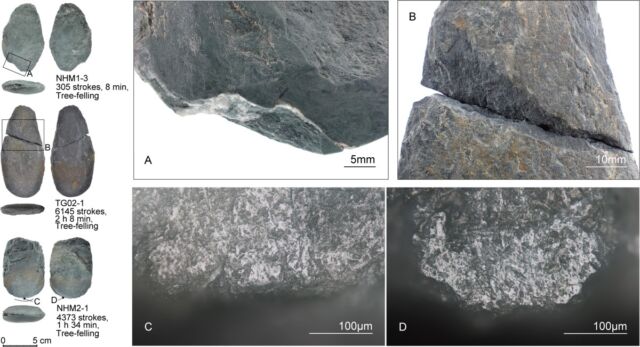
So Akira Iwase of Tokyo Metropolitan College and co-authors made their very own replicas of adzes and axes out of three uncooked supplies widespread to the area between 38,000 and 30,000 years in the past: semi-nephrite rocks, hornfels rocks, and tuff rocks. They used a stone hammer and anvil to create numerous lengthy oval shapes and polished the sides with both a coarse-grained sandstone or a medium-grained tuff. There have been three kinds of duplicate instruments: adze-types, with the working edge oriented perpendicular to the lengthy axis of a bent deal with; axe-types, with a working edge parallel to the bent deal with’s lengthy axis; and chisel-types, by which a stone software was positioned on the finish of a straight deal with.

A. Iwase et al., 2024/Tokyo Metropolitan College
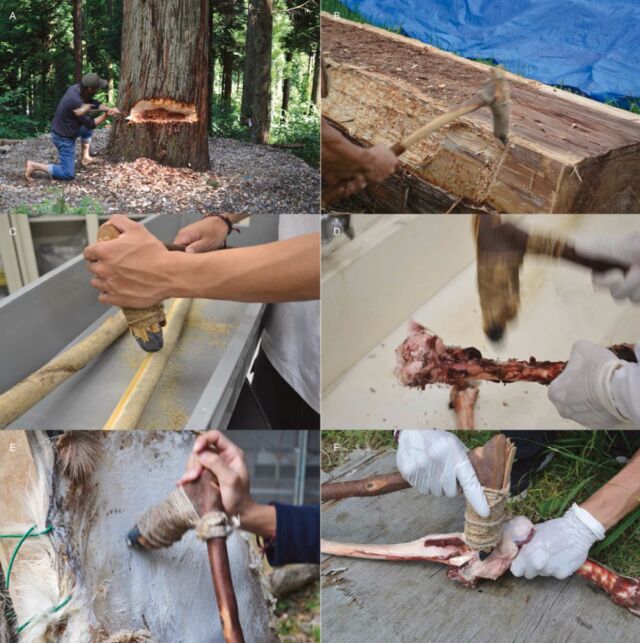
Then it was time to check the duplicate instruments by way of ten completely different utilization experiments. As an illustration, the authors used axe-type instruments to fell Japanese cedar and maple bushes in north central Honshu, in addition to a forest close to Tokyo Metropolitan College. Axe-type and adze-type instruments have been used to make a dugout canoe and picket spears, whereas adze-type instruments and chisel-type instruments have been used to scrape off the bark of fig and pine. They scraped flesh and grease from recent and dry hides of deer and boar utilizing adze-type and chisel-type instruments. Lastly, they used adze-type instruments to disarticulate the femur and tibia joints of deer hindlimbs.
The staff additionally carried out a number of experiments by which the instruments weren’t used to establish unintended fractures not associated to any tool-use perform. As an illustration, flakes and blades can break in half throughout flint knapping; transporting instruments in, say, small leather-based luggage could cause microscopic flaking; and trampling on instruments left on the bottom also can modify the sides. All these situations have been examined. All of the instruments utilized in each use and non-use experiments,ents have been then examined for each macroscopic and microscopic traces of fracture or put on.
Tokyo Metropolitan College
The outcomes: they have been capable of establish 9 several types of macroscopic fractures, a number of of which have been solely seen when making percussive motions, significantly within the case of felling bushes. There have been additionally telltale microscopic traces ensuing from friction between the wooden and stone edge. Reducing away at antlers and bones induced lots of injury to the sides of adze-like instruments, creating lengthy and/or broad bending fractures. The instruments used for limb disarticulation induced pretty massive bending fractures and smaller flaking scars, whereas solely 9 out of 21 of the scraping instruments confirmed macroscopic indicators of damage, regardless of a whole lot of repeated strokes.
The authors concluded that analyzing macroscopic fracture patterns alone are inadequate to find out whether or not a given stone software had been used percussively. Neither is any ensuing micropolish from abrasion an unambiguous indicator by itself, since scraping motions produce an identical micropolish. Combining the 2, nonetheless, did yield extra dependable conclusions about which instruments had been used percussively to fell bushes, in comparison with different makes use of, similar to disarticulation of bones.
DOI: Journal of Archaeological Science, 2024. 10.1016/j.jas.2023.105891 (About DOIs).
